Big data has revolutionized the way marketers approach their work, providing access to a wealth of information about consumer behavior, preferences, and attitudes. The five Vs of big data – volume, variety, velocity, veracity, and value – are particularly relevant to marketing, as they highlight the challenges and opportunities presented by the vast amount of data generated by modern marketing activities. This paper examines the five Vs of big data in the context of marketing, exploring the implications for marketers and the strategies they can use to make the most of big data.
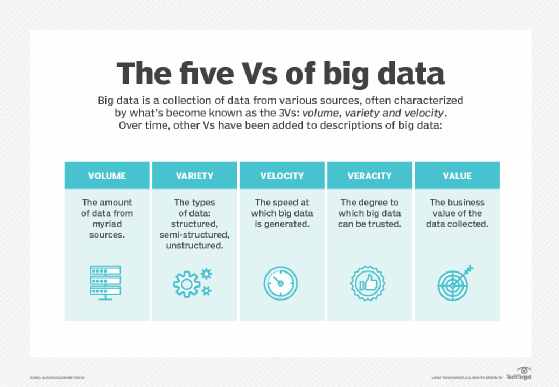
Volume
The volume of data generated by modern marketing activities is staggering. The growth of digital marketing channels such as social media, mobile apps, and e-commerce platforms has led to an explosion of data, with millions of interactions and transactions taking place every day. Marketers need to be able to handle large volumes of data to extract meaningful insights that can inform their strategies and tactics. This requires sophisticated tools and technologies, such as data warehouses, data lakes, and analytics platforms, that can process and store data efficiently.
However, the sheer volume of data can also be overwhelming for marketers. Sorting through large datasets to identify relevant information can be time-consuming and challenging, and the potential for information overload is high. Marketers need to have a clear understanding of their objectives and the types of data that are most relevant to achieving them to avoid getting bogged down in irrelevant or extraneous data.
Variety
The variety of data in marketing is also a significant challenge. Marketing data comes from a wide range of sources, including website analytics, social media metrics, email marketing campaigns, and customer relationship management (CRM) systems. Each of these sources generates different types of data, from structured data such as transactional data and customer demographics to unstructured data such as social media posts and customer reviews.
The variety of data presents significant challenges for marketers who need to be able to integrate and analyze data from multiple sources to gain a comprehensive understanding of consumer behavior. This requires a data integration strategy that can unify data from disparate sources and a data analysis strategy that can process both structured and unstructured data. Marketers also need to be able to use data visualization tools and techniques to make sense of complex data and communicate insights effectively to stakeholders.
Velocity
The velocity of data is critical for marketers who need to respond quickly to changes in consumer behavior and market trends. Social media, in particular, generates large volumes of data in real-time, making it essential for marketers to be able to monitor and respond to social media activity in real-time. Real-time data analytics tools such as dashboards and alerts are essential for marketers to be able to identify and respond to changes in consumer behavior and preferences.
However, the velocity of data also poses challenges for marketers. The sheer volume of data generated by social media and other real-time marketing channels can be overwhelming, making it challenging to identify relevant information in real-time. Marketers need to be able to filter and prioritize data to focus on the most critical insights and trends.
Veracity
The veracity of data is a critical issue in marketing, where the accuracy and reliability of data can have a significant impact on marketing strategies and tactics. The accuracy of data can be affected by a range of factors, including data quality issues, data collection biases, and inaccurate or incomplete data. Marketers need to be able to trust the data they are using to make informed decisions and avoid costly mistakes.
Veracity is particularly important in areas such as customer segmentation, where inaccurate or incomplete data can lead to poor targeting and ineffective marketing campaigns. Marketers need to be able to perform data validation and verification to ensure that the data they are using is accurate and reliable. They also need to be able to identify and correct errors and biases in data to avoid making decisions based on inaccurate information.
Value
The fifth and final V of big data in marketing is value. In many ways, value is the most important of the five Vs, as it represents the ultimate goal of all marketing activities – to create value for customers and generate value for the organization. Big data can play a critical role in delivering value to customers by enabling marketers to better understand their needs, preferences, and behaviors. It can also help organizations to optimize their marketing activities and achieve better results from their marketing investments.
Big data can create value for marketers in several ways. One way is by improving the accuracy of customer segmentation and targeting. By using data analytics tools to analyze customer data, marketers can identify patterns and trends that can be used to group customers into segments based on their shared characteristics and behaviors. This allows marketers to tailor their marketing messages and offers to each segment, increasing the relevance and effectiveness of their marketing efforts.
Big data can also be used to personalize the customer experience, creating a more engaging and relevant interaction between the customer and the organization. By tracking customer behavior and preferences, organizations can offer personalized recommendations, content, and offers that are tailored to the individual customer’s needs and interests. This not only improves the customer experience but can also lead to increased loyalty and advocacy, as customers feel valued and understood by the organization.
In addition to improving the customer experience, big data can also help organizations to optimize their marketing activities and achieve better results from their marketing investments. By using data analytics tools to analyze marketing campaign data, organizations can identify the most effective channels, messages, and offers, and adjust their marketing strategies accordingly. This can help to reduce marketing costs and improve marketing ROI, as organizations focus their efforts on the most effective channels and tactics.
However, realizing the value of big data in marketing requires a strategic approach. Marketers need to have a clear understanding of their goals and objectives, as well as the data sources and analytics tools they need to achieve them. They also need to have a deep understanding of their customers and the data that is most relevant to understanding their needs and preferences. Finally, they need to be able to effectively communicate their insights and recommendations to stakeholders, including senior management and cross-functional teams.
The five Vs of big data – volume, variety, velocity, veracity, and value – present significant opportunities and challenges for marketers. The sheer volume of data generated by modern marketing activities requires sophisticated tools and technologies to process and store data efficiently. The variety of data requires a data integration strategy that can unify data from disparate sources and a data analysis strategy that can process both structured and unstructured data.
References
Böhm, M., De Marez, L., Ballon, P., & Cottenier, T. (2016). The impact of big data on innovation in the insurance industry: A case study. Journal of Innovation Management, 4(4), 42-57.
Chen, J., & Mao, S. (2014). Big data: A survey. Mobile Networks and Applications, 19(2), 171-209.
aney, D. (2001). 3D Data Management: Controlling Data Volume, Velocity and Variety. META Group Research Note.
Manyika, J., Chui, M., Brown, B., Bughin, J., Dobbs, R., Roxburgh, C., & Byers, A. H. (2011). Big data: The next frontier for innovation, competition, and productivity. McKinsey Global Institute.
Zikopoulos, P., Eaton, C., deRoos, D., Deutsch, T., & Lapis, G. (2011). Understanding big data: Analytics for enterprise class hadoop and streaming data. McGraw-Hill Osborne Media.
