The International Market Entry Evaluation Process
How to Enter a Foreign Market
This lesson gives an outline of the way in which an organization should select which foreign to enter. The International Marketing Entry Evaluation Process is a five stage process, and its purpose is to gauge which international market or markets offer the best opportunities for our products or services to succeed. The five steps are Country Identification, Preliminary Screening, In-Depth Screening, Final Selection and Direct Experience. Let’s take a look at each step in turn.
Step One – Country Identification
The World is your oyster. You can choose any country to go into. So you conduct country identification – which means that you undertake a general overview of potential new markets. There might be a simple match – for example two countries might share a similar heritage e.g. the United Kingdom and Australia, a similar language e.g. the United States and Australia, or even a similar culture, political ideology or religion e.g. China and Cuba. Often selection at this stage is more straightforward. For example a country is nearby e.g. Canada and the United States. Alternatively your export market is in the same trading zone e.g. the European Union. Again at this point it is very early days and potential export markets could be included or discarded for any number of reasons.
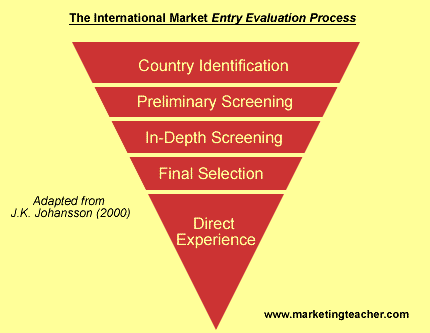
Step Two – Preliminary Screening
At this second stage one takes a more serious look at those countries remaining after undergoing preliminary screening. Now you begin to score, weight and rank nations based upon macro-economic factors such as currency stability, exchange rates, level of domestic consumption and so on. Now you have the basis to start calculating the nature of market entry costs. Some countries such as China require that some fraction of the company entering the market is owned domestically – this would need to be taken into account. There are some nations that are experiencing political instability and any company entering such a market would need to be rewarded for the risk that they would take. At this point the marketing manager could decide upon a shorter list of countries that he or she would wish to enter. Now in-depth screening can begin.
Step Three – In-Depth Screening
The countries that make it to stage three would all be considered feasible for market entry. So it is vital that detailed information on the target market is obtained so that marketing decision-making can be accurate. Now one can deal with not only micro-economic factors but also local conditions such as marketing research in relation to the marketing mix i.e. what prices can be charged in the nation? – How does one distribute a product or service such as ours in the nation? How should we communicate with our target segments in the nation? How does our product or service need to be adapted for the nation? All of this information will form the basis of segmentation, targeting and positioning. One could also take into account the value of the nation’s market, any tariffs or quotas in operation, and similar opportunities or threats to new entrants.
Step Four – Final Selection
Now a final short-list of potential nations is decided upon. Managers would reflect upon strategic goals and look for a match in the nations at hand. The company could look at close competitors or similar domestic companies that have already entered the market to get firmer costs in relation to market entry. Managers could also look at other nations that it has entered to see if there are any similarities, or learning that can be used to assist with decision-making in this instance. A final scoring, ranking and weighting can be undertaken based upon more focused criteria. After this exercise the marketing manager should probably try to visit the final handful of nations remaining on the short, short-list.
Step Five – Direct Experience
Personal experience is important. Marketing manager or their representatives should travel to a particular nation to experience first hand the nation’s culture and business practices. On a first impressions basis at least one can ascertain in what ways the nation is similar or dissimilar to your own domestic market or the others in which your company already trades. Now you will need to be careful in respect of self-referencing. Remember that your experience to date is based upon your life mainly in your own nation and your expectations will be based upon what your already know. Try to be flexible and experimental in new nations, and don’t be judgemental – it’s about what’s best for your company – happy hunting.
