Positioning
The third and final part of the SEGMENT – TARGET – POSITION (STP) process is ‘positioning.’ Positioning is undoubtedly one of the simplest and most useful tools to marketers. After segmenting a market and then targeting a consumer, you would proceed to position a product within that market.
The term ‘positioning’ refers to the consumer’s perception of a product or service in relation to its competitors. You need to ask yourself, what is the position of the product in the mind of the consumer?
Remember this important point. It is all about ‘perception’. As perception differs from person to person, so do the results of the positioning map e.g what you perceive as quality, value for money, etc, is different to my perception. However, there will be similarities.
Products or services are ‘mapped’ together on a ‘positioning map‘. This allows them to be compared and contrasted in relation to each other. This is the main strength of this tool. Marketers decide upon a competitive position which enables them to distinguish their own products from the offerings of their competition.
Take a look at the basic positioning map template below.
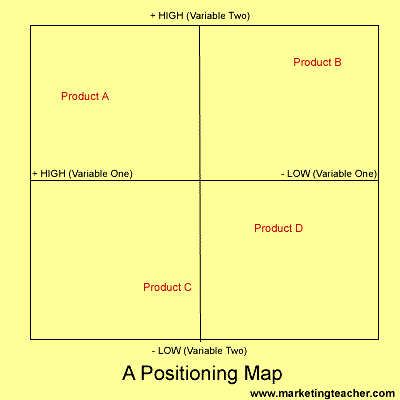
The marketer would draw out the map and decide upon a label for each axis. They could be price (variable one) and quality (variable two), or Comfort (variable one) and price (variable two). The individual products are then mapped out next to each other Any gaps could be regarded as possible areas for new products.
Trout and Ries suggest a six-step question framework for successful positioning:
1. What position do you currently own?
2. What position do you want to own?
3. Whom you have to defeat to own the position you want.
4. Do you have the resources to do it?
5. Can you persist until you get there?
6. Are your tactics supporting the positioning objective you set?
Look at the example below using the auto market.
Product: Ferrari, BMW, Kia, Range Rover, Saab, Hyundai.
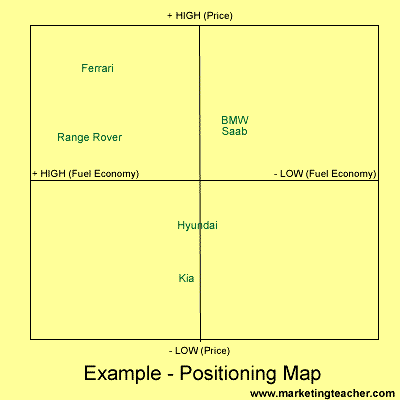
Positioning Map for Cars.
The six products are plotted upon the positioning map. It can be concluded that products tend to bunch in the high price/low economy(fast) sector and also in the low price/high economy sector. There is an opportunity in the low price/ low economy (fast) sector. Maybe Hyundai or Kia could consider introducing a low cost sport saloon. However, remember that it is all down to the perception of the individual.
